Here we’ll be looking at Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords): Google’s own advertising service which allows you to place search results for your website on a search engine results page (SERP) by paying for them.
There’s no need to wait for your new site to work its way organically up the rankings. By using paid search you can see immediate results and it’s not nearly as difficult to use or expensive as you may think.
Paid search
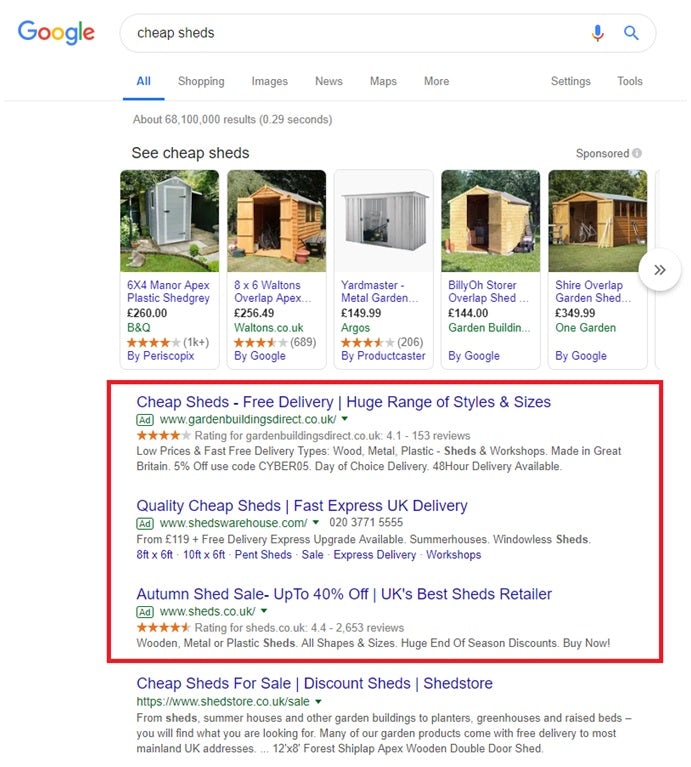
Paid search is the term we use for advertising within the listings of a search engine. These normally appear at the top of a SERP or to the side, and increasingly look more and more like organic results. At the moment Google places a small green ‘Ad’ label on them.

Google isn’t the only search engine where you can do this; Bing also runs its own advertising network, called The Bing Network.
You can read more about paid search and the different ways to go about it in our beginner’s guide to paid search: ‘What is paid search (PPC) and why do you need it?’
But for the purposes of this piece, we’re going to focus on Google Ads. Let’s take a look at how it works.
Basic principles of Google Ads
In a nutshell, you pick some keywords that a searcher might use on Google, then create an advert that will appear on the SERP based on those keywords.
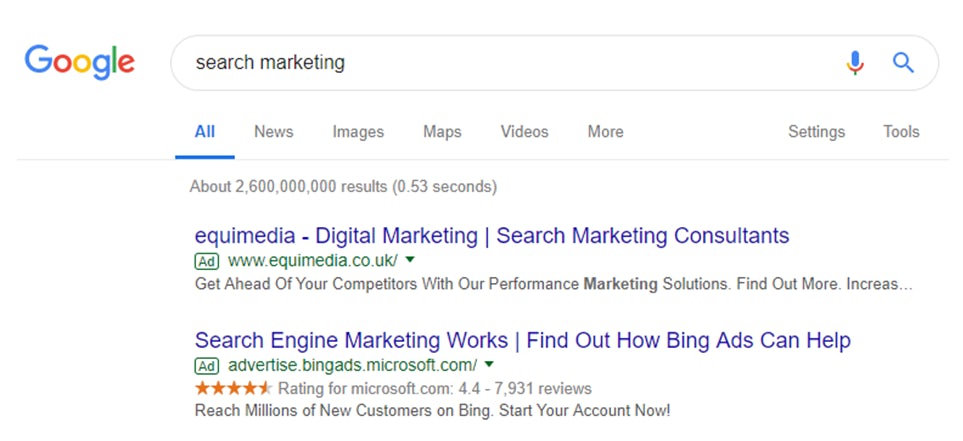
Of course you’re probably not going to be the only company wanting to serve adverts to people who use those particular terms. Rival companies can bid for the same search term.
Of course, you’re probably not going to be the only company wanting to serve adverts to people who use those particular terms. Rival companies can bid for the same search term.
If you want your ad to appear at all, you have to bid against other marketers on how much you’re willing to pay Google Ads every time a searcher clicks on your ad.
The more you pay per click, the more likely your ad will appear in the search results (which is why paid search is often referred to as PPC, which stands for Pay-Per-Click).
However, and this is a big however, unlike other real-time bidding models, it’s not just the highest bid that is taken into account. To determine how high your ad appears up the SERP and whether it’s shown at all, Google will assign it something called an ‘Ad Rank’.
What is Ad Rank?
Ad Rank is a metric that Google uses to determine the order in which paid search ads are displayed on the SERP. Per Google Ads Help:
“Generally speaking, the ad with the highest Ad Rank gets to show in the top position and the ad with the second-highest Ad Rank gets to show in the second position (assuming the ads clear the relevant thresholds), and so on.”
Your bid amount is just one of five factors that go into calculating Ad Rank. Other factors include:
- The quality of your ads and landing page (reflected in your Quality Score)
- The Ad Rank thresholds, a set of quality thresholds your ad needs to meet in order to be eligible to show. These can depend on things like the topic and nature of a search, location, and device type
- Search context, including the query, the time of the search, the other ads and search results that show on the page, and other user signals like location and device type
- Ad extensions and other ad formats: these are the pieces of additional information you can add such as a phone number, or more links to other pages on your website.
AdWords conversion linker: What is it and why do you need it?
Bidding
You pay Google Ads each time your ad is clicked. The price you’re willing to pay for each click is called cost-per-click (CPC).
You can pick a maximum bid amount, and if you choose the automatic option, Google chooses the bid amount for you within your budget, and theoretically brings you the most clicks possible within that budget.
There is also another less common option called cost per impression (CPM). This is where you pay the search engine for every 1,000 times your ad appears on the SERP. The user doesn’t have to click through.
You can choose between either method.
The time it takes for Google Ads to look at all the relevant advertisers bidding for a search term, decide whether there will be an auction or not, hold that auction, work out which ad offers a mixture of highest maximum bid + quality score and finally serves that ad on the results page, is the time it takes for someone to type a search term into Google and receive the results.
Which is about 0.26 seconds.
Alternatives to Google Ads
The Bing Network: Formerly known as the Yahoo Bing Network, the Bing Network is the ad network belonging to Bing, Google’s biggest search engine rival. A number of syndicated partners make up the Network, including AOL, the Wall Street Journal and Gumtree.
According to statistics from Bing Ads, the Bing Network currently has a 33.9% market share in the US, and 24.7% in the UK, meaning that it reaches a not insignificant portion of searchers who may not be reachable via Google Ads.
Search Engine Optimisation (SEO): This term refers to all the methods, tactics and processes by which you can increase the likelihood of your website appearing and ranking well in the organic (non-paid) search engine results. If you employ cracking SEO, then you may not even need to use paid search. However, many marketers will recommend that both are vital to search marketing and complement each other effectively.
Google Shopping: You may have noticed in the example at the top of the page a carousel showing sponsored shopping results.
You can submit listings such as this to Google Ads, by creating Product Listing Ads (PLA) featuring relevant details, rich images, product prices and your store name. For a detailed guide on how to get set up with Google Shopping, read our PPC Best Practice Guide section on Google Shopping.
Learn more
For many more insights into paid search strategy and best practice, download Econsultancy’s Paid Search Best Practice Guide.

Nice article and thank you for this valuable information